Key Takeaway
- Cloud-native applications are elastic, scalable, and cost-efficient and allow for flexible use of resources.
- They implement automation and DevOps practices enabling faster delivery, like CI/CD, orchestration, and infrastructure as code.
- Microservices and serverless architectures enable modular, maintainable, and independently deployable services.
- The main challenges include complexity, security, cost, monitoring, and vendor lock-in.
- Best practices include adopting DevSecOps, selecting appropriate technology stacks, implementing multi-layered security, and continuous monitoring and deployment.
Market Analysis of Global Cloud-Native Application Development
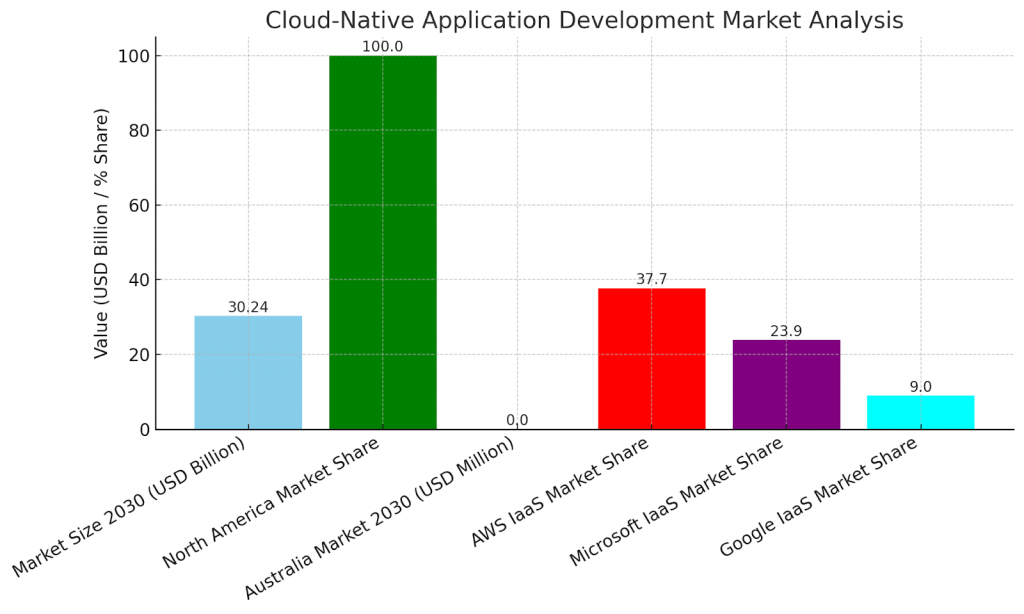
- The market for cloud-native application development is increasing rapidly at a projected USD 30.24 billion by 2030, growing at a CAGR of 23.8% from 2024 to 2030.
- North America holds a significant market share, driven by the U.S. market. The fastest-growing regional market is Australia, expected to reach USD 919.4 million by 2030.
- Technology drivers include platform engineering, Kubernetes native data services, growing generative AI workload, and GPU consumption for AI training.
- Platforms represent a significant amount of revenue in 2024, while services are the fastest-growing segment over the forecast period.
- AWS dominates the IaaS market, with a 37.7% market share. Microsoft and Google are gaining market share at 23.9% and 9% market share, respectively.
Introduction of Cloud-Native Application development
The way we develop and run software applications today is best described as cloud-native application development, taking full advantage of cloud computing. Whereas an application running in the cloud might be considered – simply another hosting platform, cloud-native development focuses on building applications specifically for cloud computing, which is dynamic, manageable and distributed.
Key Benefits of Cloud-Native Apps
- Scalability – This enables cloud-native applications to automatically increase or decrease resources in response to demand, ensuring that performance remains consistent during traffic spikes and efficiently computes resource consumption.
- Agility and Flexibility – They facilitate faster development, faster deployment, and the ability to provide updates sooner. Organizations can respond to changes in the market rapidly and deploy features to users with little to no lag time.
- Cost Efficiency – Leveraging cloud resources on a paid service subscription basis can significantly reduce costs, including infrastructure and maintenance costs, making operations more efficient, cost-effective, and resource-efficient.
- Resilience and Reliability – Cloud-native applications are designed with self-healing capabilities to deal with failures, resulting in little downtime and service continuity for the user.
- Improved Performance and Security – In addition, cloud-native applications can offer optimized performance, resulting in decreased response times. They include modern security practices including patching automation and secure access controls to help keep users’ applications and data secure.
Core principle of Cloud Native Application Development
- Microservices Architecture – Instead of a single application, software is created as separate services that can be developed, deployed, and scaled independently of the other services. This approach provides flexibility and speed when deploying a software update.
- Containerization – Services developed as microservices run in their own container to promote consistency across development, testing, and production each environment and to enhance portability.
- Dynamic Orchestration – Tools like Kubernetes deploy and manage containers automatically, including scaling, load balancing, and self-healing, to keep operations running smoothly regardless of failures.
- API-First Design – Each service communicates with other services via a well-defined Application Programming Interface (API) to facilitate seamless integration and interoperability and to allow for faster adoption of other technologies.
- Continuous Integration and Continuous Deployment (CI/CD) – Automated pipelines allow developers to deploy code frequently, reliably, and rapidly, to promote increased innovation and decrease downtime.
How To Develop a Cloud-Native Application
- Determine and Specify Requirements: Considering purpose, user base, and specific functions of the application. Determine what scalability, performance, and security requirements are needed in order to steer architectural decisions.
- Design with Microservices Architecture In Mind: Break the application up into smaller and self-contained pieces of functionality so that it can be developed, tested, and deployed individually.
- Choose Cloud Provider and Containers: Pick cloud provider (eg. AWS, Azure, GCP) and consider running the microservices in containers (like Docker) to provide portability, consistency and reduce redundancy across environments.
- Implement CI/CD Pipelines: Create a CI/CD pipeline for the app to develop and test continuously and deploy the code automatically will allow for expedited application updates, testing and, finding issues while maintaining reliability.
- Deploy, Monitor and Optimize: Use orchestration tools like Kubernetes for deployment, auto-scale and load balance the application. Continuously monitor and troubleshoot performance and optimize resource utilization.
Why Cloud-Native is the Future of Development ?
- Rapid Innovation – Cloud-native allows for enhanced velocity in both development and deployment. Organizations can quickly roll out new functionalities and features, quickly react to rapidly-changing market conditions, and outperform their competition.
- Scalability on Demand – Applications can rapidly scale to accommodate peaks in user traffic or workload. This means there is no need to over-provision resources, while ensuring that performance meets expectations at peak times.
- Cost Efficiency – Pay-as-you-go cloud pricing models reduce up-front infrastructure costs. Organizations only pay for what they use, making both development and operations significantly more affordable.
- Resilience and Reliability – Cloud-native applications are built to withstand failure with self-healing and redundancy. This translates to less downtime and ensures that services are available 100% of the time.
- Support for New Technologies – Cloud-native architecture is designed to work in combination with AI, ML, IoT, and other emerging technology. This helps to future-proof applications and stay competitive in the market.
Conclusion
Cloud-native application development is revolutionizing how software is developed, deployed, and managed. By employing cloud infrastructure, microservices, and containers, organizations can achieve greater scalability, flexibility, and resilience. It represents the best way to build applications for the future, because it is conducive to accelerated innovation and cost efficiency as well as improved compatibility with emerging technologies. By embracing cloud-native approaches, organizations can remain competitive, responsive, and ready for changing market demands. Choose the best mobile app development company in the USA.
Important FAQs
What is a cloud-native application?
A cloud-native application is designed and built specifically to run in cloud environments. It leverages microservices, containers, and dynamic orchestration for scalability, flexibility, and resilience.
Why choose cloud-native over traditional applications?
Cloud-native apps allow faster development, automatic scaling, cost efficiency, and higher reliability compared to traditional monolithic applications.
Which technologies are commonly used in cloud-native development?
Key technologies include Docker (for containerization), Kubernetes (for orchestration), microservices architecture, CI/CD pipelines, and cloud platforms like AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud.
Is cloud-native suitable for small businesses?
Yes, even small businesses benefit from cloud-native development because of its scalability, cost-efficiency, and ability to rapidly deploy new features without heavy infrastructure investment.
What are the challenges in cloud-native development?
Challenges include managing microservices complexity, ensuring security, monitoring distributed systems, and requiring skilled developers familiar with cloud-native tools.
Also Read
StreamEast App: Complete Guide, Safety Check & Alternatives Apps








 sales@doomshell.com
sales@doomshell.com
 +91 8005523567
+91 8005523567



